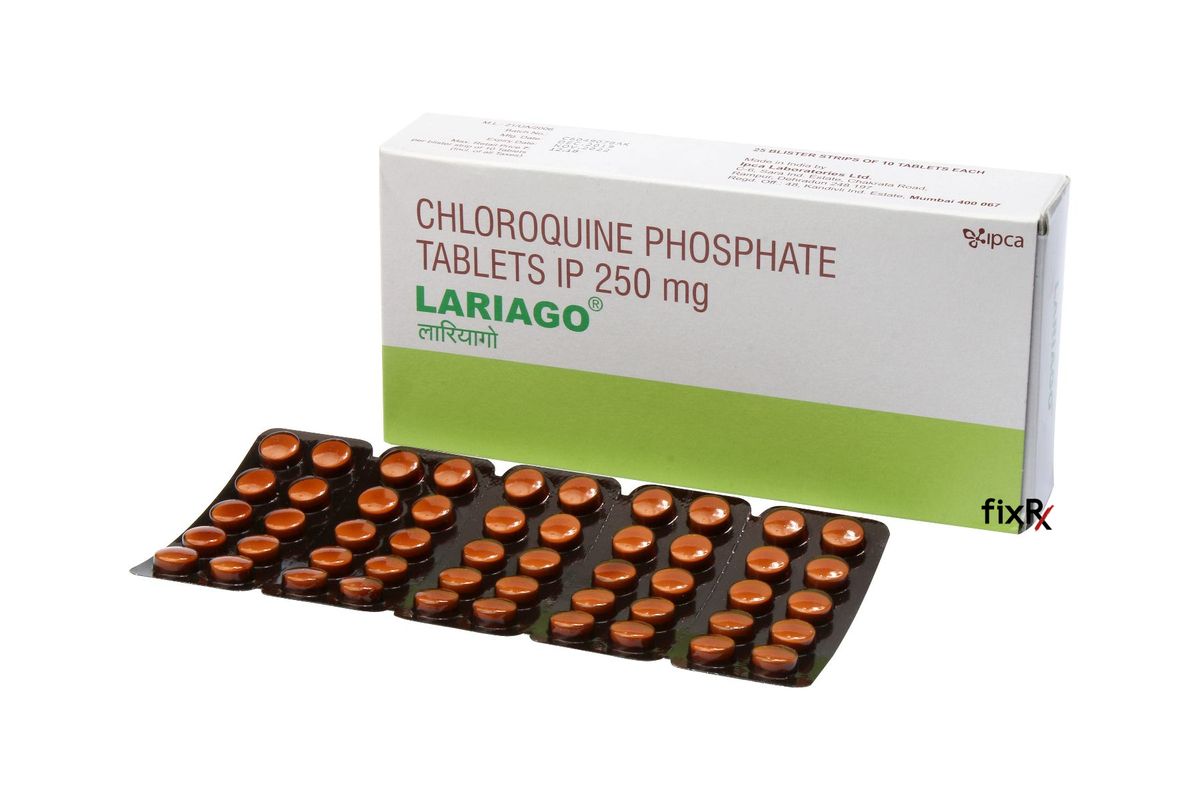
Description
Chloroquine 250 mg is an antimalarial medication primarily used to prevent and treat malaria caused by the Plasmodium parasite. It is also used in the treatment of certain autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus erythematosus. Chloroquine works by inhibiting the growth of the malaria parasite in red blood cells, preventing it from reproducing.
The typical dosage for malaria prevention is usually 250 mg once a week, starting one to two weeks before traveling to an area where malaria is common and continuing for several weeks after returning. For treatment of malaria, the dosage is higher, and the regimen often involves multiple doses over a period of several days. For autoimmune diseases the dosage varies and is typically based on the patient’s condition and the physician’s recommendation.
Chloroquine is generally well-tolerated, but it can cause side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, headache, dizziness and skin rashes. Long-term use or high doses can lead to more serious effects, including vision problems, muscle weakness, and heart rhythm disturbances. It is important for patients to have regular eye exams while on long term chloroquine therapy to monitor for retinal damage.
Chloroquine should be used with caution in people with liver or kidney disease, and it may interact with other medications, such as antacids and certain antibiotics. It is also important to note that chloroquine should not be used in individuals with a known allergy to the drug or those with certain heart conditions, such as prolonged QT syndrome.
In the case of overdose, symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, confusion, and in severe cases, seizures, respiratory distress, or cardiac arrest. Overdose requires immediate medical attention. If stopping the medication, it should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider, particularly in the case of long-term use.
Chloroquine is not effective against all types of malaria, especially those caused by Plasmodium falciparum, which is resistant to chloroquine in some regions. In such cases, other antimalarial medications may be used. It is also not effective for treating malaria in areas with high drug resistance



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.